In any business ecosystem, streamlining and systemizing procurement processes are paramount for efficient operations and cost management. Among the various instruments employed to achieve this, the purchase order (PO) stands out as a critical tool. This article provides a comprehensive understanding of what a purchase order is, its primary purpose, its functioning, the types of purchase orders, how to create one, examples of purchase order formats, best practices for handling them, methods to track them, their importance, benefits, and the role of automation in their creation.
What Is a Purchase Order?
A purchase order, commonly abbreviated as PO, is a commercial and legal document issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services. It serves as an offer document that becomes a legally binding contract once the seller approves it.
Essentially, a purchase order acts as an official order form, covering details of the items or services requested, delivery schedules, payment terms, and other associated information. This document plays a critical role in ensuring the buyer gets precisely what they’ve requested, and the seller has a clear roadmap of what they need to provide.
The Core Purpose of a Purchase Order
A purchase order primarily serves as a legally binding document that outlines the particulars of a business transaction between a buyer and a vendor. Once a vendor accepts a purchase order, it becomes a legal contract safeguarding both parties involved.
From a buyer’s perspective, the primary purpose of a purchase order is to specify their requirements in terms of goods or services. It forms the basis of understanding for the vendor about what they need to deliver and at what cost. A purchase order also provides an audit trail within the buyer’s procurement system, aiding in tracking and managing orders.
From the vendor’s perspective, a purchase order gives the necessary authorization to deliver the requested goods or services, ensuring they get paid for their efforts.
How Does a Purchase Order Work?
The process of creating and processing a purchase order involves several stages. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a purchase order works:
Initiation
The process typically begins with an internal need within an organization, prompting the creation of a purchase requisition. This could stem from various departments such as procurement, operations, or project management.
Creation
Upon approval of the requisition, a purchase order is generated. This document outlines the details of the requested goods or services, including quantities, specifications, prices, delivery terms, and payment terms.
Review and Approval
The purchase order undergoes review and approval within the organization to ensure compliance with procurement policies, budgetary constraints, and other relevant guidelines.
Issuance
Once approved, the purchase order is issued to the selected vendor, communicating the organization’s intent to procure the specified goods or services.
Acknowledgment
Upon receipt of the purchase order, the vendor acknowledges its receipt and may confirm acceptance of the terms and conditions outlined in the document.
Fulfillment
The vendor reviews the purchase order to ensure they can fulfill the requested goods or services within the specified timeframe and according to the agreed-upon terms.
Once confirmed, the purchase order becomes a legally binding contract between the buyer and the vendor.
Shipment/Service Delivery:
If the purchase order involves physical goods, the vendor proceeds to package and dispatch the items to the buyer’s designated delivery address.
For service-based purchase orders, the vendor initiates the agreed-upon services as outlined in the purchase order.
Receipt and Verification
Upon receiving the goods or services, the buyer verifies them against the details specified in the purchase order. Any discrepancies are communicated with the vendor for resolution.
Invoicing and Payment
After successful delivery or completion of services, the vendor issues an invoice to the buyer.
The buyer processes the invoice for payment based on the agreed-upon payment terms, completing the purchase order process.
Recordkeeping
Both the buyer and the vendor maintain records of the purchase order and related transactions for accounting and auditing purposes.
This systematic workflow ensures that the procurement process is efficient, transparent, and legally binding for both parties involved.
Types of Purchase Orders
There are several types of purchase orders, each serving a unique purpose and used under different circumstances. Let’s explore the primary ones:
Standard Purchase Orders
These are the most commonly used purchase orders. They’re typically used for one-time purchases and include all the necessary details like item descriptions, quantities, prices, and delivery dates.
Blanket Purchase Orders
These orders are used when there’s a recurring need for a product or service. A blanket purchase order specifies a set of goods or services to be provided over a certain period, offering flexibility in terms of quantities and delivery schedules.
Contract Purchase Orders
Contract Purchase Orders also known as standing purchase orders, these are long-term agreements that set the terms and conditions for future transactions. These don’t specify quantities or delivery dates, which are determined in subsequent standard purchase orders referring to the contract purchase order.
Planned Purchase Orders
These are long-term purchase agreements that outline the goods or services to be procured over a period. They include estimated quantities and delivery schedules but require release orders to initiate actual purchases.
Electronic Purchase Orders
As the name suggests, these are digital versions of traditional purchase orders. They’re created, processed, and tracked using specialized software, offering greater efficiency and accuracy.
Single Purchase Orders
These purchase orders are used for one-time procurement needs, such as acquiring a specific product or service for a particular project or requirement. They contain all the necessary details of the transaction, similar to standard purchase orders.
Direct Purchase Orders
Direct purchase orders involve buying goods directly from a supplier without involving intermediaries like distributors or wholesalers. This allows for more direct communication and negotiation between the buyer and the supplier, potentially reducing costs and streamlining the procurement process.
Emergency Purchase Orders
Emergency purchase orders are issued in urgent situations where immediate procurement is necessary to address critical needs or unexpected circumstances. These orders prioritize speed and may bypass standard approval processes to ensure timely acquisition of goods or services.
Drop-Ship Purchase Orders
Drop-ship purchase orders occur when a buyer purchases goods from a supplier but requests the supplier to directly ship the goods to the buyer’s customer. This arrangement eliminates the need for the buyer to handle inventory and shipping logistics, making it ideal for e-commerce businesses or companies with limited storage space.
Reverse Purchase Orders
Reverse purchase orders are used for returning goods to a supplier due to defects, damages, or overstock. They facilitate the return process by documenting the items being returned, the reason for return, and any associated restocking fees or credits.
Framework Purchase Orders
Framework purchase orders establish framework agreements between a buyer and a supplier for the supply of goods or services over a specified period. Unlike standard purchase orders, framework purchase orders typically outline the general terms and conditions of the agreement, with specific quantities and delivery schedules determined through subsequent call-off orders.
Milestone Purchase Orders
Milestone purchase orders are structured around specific project milestones, with payments made based on the achievement of predetermined milestones rather than upon completion of the entire project. These orders provide a structured approach to project management and payment processing, allowing for better alignment of payments with project progress and deliverables.
The Benefits of Purchase Orders
Using purchase orders offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Accountability: Purchase orders provide a clear audit trail, enhancing accountability and transparency in procurement.
- Improved Financial Control: Purchase orders enable better financial control by ensuring that purchases are made within budget and approved by authorized personnel.
- Efficient Record Keeping: Purchase orders facilitate efficient record-keeping, which is crucial for audit purposes, dispute resolution, and financial management.
- Better Supplier Relationships: Purchase orders help establish clear expectations with suppliers, leading to better relationships and smoother transactions.
- Optimized Procurement Process: Purchase orders streamline the procurement process, making it more efficient and effective.
How to Create a Purchase Order
Creating a purchase order is a straightforward process, especially when using a digital platform. Here are the key steps involved:
- Identify the Need: The process begins when a department or individual in your organization identifies a need for goods or services.
- Create the Purchase Requisition: The identified need is then formalized through a purchase requisition, which is sent for approval.
- Generate the Purchase Order: Once the requisition is approved, a purchase order is created. This document includes critical details like the type of product or service, quantity, price per unit, total cost, delivery schedule, and payment terms.
- Send the Purchase Order: The purchase order is then sent to the vendor. This can be done through email or a dedicated procurement platform if you’re using one.
- Track the Purchase Order: After issuing the purchase order, it’s crucial to track it until the order is fulfilled. This involves monitoring the dispatch, delivery, and invoice payment stages.
Purchase Order Format Examples
A well-designed purchase order should be easy to read and understand. It should contain all the necessary details to ensure smooth processing. Here’s a list of key elements that a typical purchase order format includes:
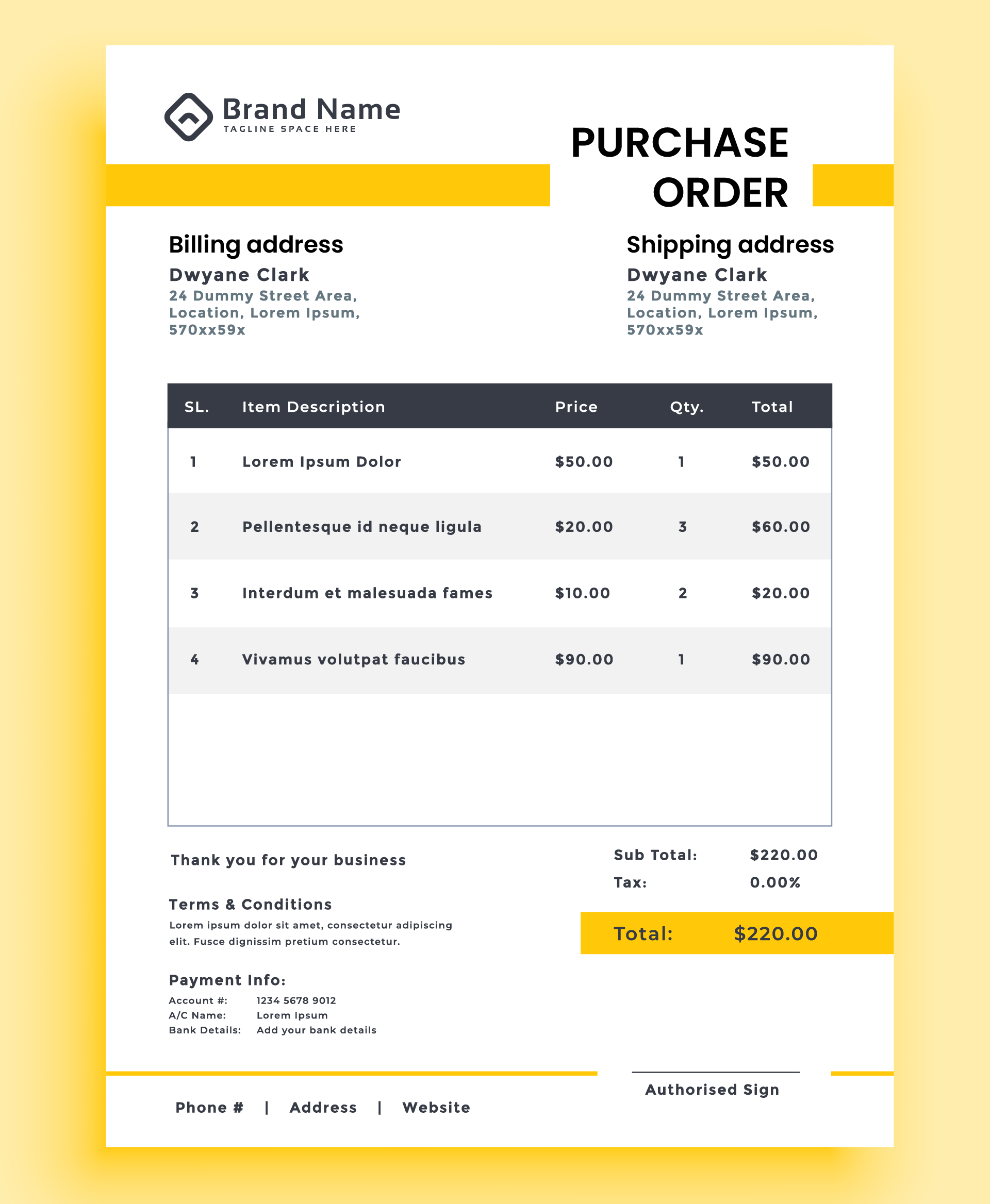
- Purchase Order Number: A unique identifier for tracking the order.
- Order Date: The date when the order was placed.
- Vendor Information: Details about the supplier, including their name, address, contact information, and location(s).
- Bill To Information: Details about where the invoice should be sent for payment, including the name, address, and contact information of the billing entity.
- Ship-To Information: Details about where the goods should be delivered.
- Description of Goods/Services: Detailed descriptions of the items or services ordered, including quantities and unit prices.
- Total Price: The total cost of the order, calculated as the product of quantities and unit prices.
- Payment Terms: The agreed-upon terms for payment, such as due date and penalties for late payment.
- Shipping Instructions: Any specific instructions for the delivery of the goods.
- Additional Terms and Conditions: Any other terms or conditions related to the order.
It’s worth noting that many businesses use digital platforms to generate purchase orders, which often come with customizable templates to suit their specific needs.
Best Practices for Handling Purchase Orders
To optimize the effectiveness of purchase orders, it’s essential to follow certain best practices. Here are some of the key ones:
Automate the Process
Using a dedicated procurement solution like Zapro can drastically improve the efficiency and accuracy of your purchase order process. Automation reduces the likelihood of manual errors and streamlines communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
Use Standard Templates
Standardized purchase order templates ensure uniformity and completeness in the information captured, making it easier to process and track orders.
Assign Clear Responsibilities
Clearly define who is responsible for creating, approving, issuing, and tracking purchase orders. This clarity helps ensure accountability and smooth process flow.
Communicate Effectively with Vendors
Foster open and clear communication with vendors. Ensure they understand your purchase order process and the information you provide in your orders.
Monitor and Track Orders
Regularly monitor the status of your purchase orders. This practice helps identify bottlenecks or delays and allows for timely corrective action.
Review and Reconcile
Regularly compare purchase orders with invoices and delivery receipts to ensure accuracy. This practice helps prevent overpayments and discrepancies in billing.
Maintain Accurate Records
Keep accurate and up-to-date records of all purchase orders, invoices, and related documentation. This practice is essential for audit purposes and resolving disputes.
What is the best way to track purchase orders?
Tracking purchase orders is vital for effective procurement management. Here are some methods for tracking purchase orders:
- Use a Centralized Procurement Platform: A centralized procurement platform offers real-time tracking of all purchase orders, providing greater visibility and control over the procurement process.
- Implement an Automated Tracking System: Automated tracking systems can generate alerts for delayed or at-risk orders, enabling you to proactively manage issues and ensure timely delivery.
- Use a Spreadsheet or Tracking Tool: For smaller businesses or those not ready for a full-fledged procurement solution, a simple spreadsheet or tracking tool can be used. However, this manual method can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
The Significance of Purchase Orders for Your Business
Purchase orders play a critical role in business operations for several reasons:
- Control and Accuracy: Purchase orders establish a structured and controlled process for procurement, ensuring all purchases are authorized and accounted for.
- Cost Management: Purchase orders help manage costs by confirming that funds are available for purchases, preventing overspending, and enabling better budgeting.
- Inventory Management: Purchase orders aid in tracking inventory and managing supply chain operations. They help ensure timely procurement of necessary goods or services, minimizing disruptions to operations.
- Cash Flow Management: Purchase orders can help manage cash flow by confirming that there are sufficient funds available to pay for purchases.
- Dispute Resolution: In case of conflicts with suppliers, a purchase order serves as a clear record of what was ordered, thus facilitating quicker and more efficient resolution.
Why do you need to automate your purchase order process?
Automation in purchase order creation is a game-changer in the realm of procurement management. Here’s why you should consider it:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation streamlines the purchase order process, reducing manual work, improving speed, and boosting overall productivity.
- Improved Accuracy: Automation minimizes manual errors, ensuring that purchase orders are accurate and complete.
- Better Visibility: Automation provides real-time visibility into the status of purchase orders, enabling quicker identification and resolution of issues.
- Cost Saving: Automation reduces the costs associated with manual and paper-based processes, such as printing, storage, and shipping.
- Enhanced Compliance: Automated systems can enforce compliance with company policies and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Among the various tools available for automating purchase order creation, Zapro stands out with its intuitive and robust features. Zapro’s dedicated procurement solution drastically improves the efficiency and accuracy of your purchase order process, offering a seamless platform for creating, processing, and tracking electronic purchase orders.
Try Zapro.ai
Purchase orders are a vital instrument in procurement management, offering a myriad of benefits, from cost control to improved supplier relationships. While their creation and management can be a complex task, automation tools like Zapro can significantly simplify the process, making purchase orders a powerful ally in your quest for efficient and effective procurement management. By leveraging Zapro’s advanced features, the intricate task of handling purchase orders becomes remarkably simplified. Zapro not only streamlines the creation and management of purchase orders but also transforms them into a potent asset in your pursuit of efficient and effective procurement management.
Ready to witness the transformative power of Zapro in action? Schedule a demo today and embark on a journey to elevate your procurement processes to new heights. Let us show you firsthand how Zapro can be your trusted ally in achieving procurement excellence.
