Why do businesses continue to use manual accounts payable systems? We asked a few business owners, and the most common reasoning we heard was that manual processes work just fine and do not have a difficult learning curve for adoption.Â
But a deeper look revealed an entirely different story. Most users employing dated systems were facing a pattern of similar issues, primarily because while it seems to be a simple process, it is far from it.
In reality, manual AP processes are needlessly complex, labor-intensive, error-prone, and tedious, often costing businesses valuable time and money. It might enable you to do an adequate job despite its shortcomings, but that’s as far as manual process capabilities go.Â
On the other hand, those engaged in accounts payable automation found that they can quickly enhance accuracy, speed up processing, improve visibility and control, compliance, increase security, simplify audits, seamlessly integrate with their existing ERP systems and build strong relationships with vendors and suppliers.Â
In such cases, AP Automation provided the businesses and their AP departments with exceptional results that manual systems could come nowhere close to delivering.
Not convinced? Stay with us as we dive into accounts payable automation, its workings, how it differs from manual AP processes, and how to implement it for your organization. Through this informative read, we will help you make an informed decision that could save time, diminish costs, and introduce a level of accuracy in your accounts payable process like you have never experienced before.
In this article, we will cover:
- What is accounts payable automation?
- How does AP automation work?
- Manual vs Automated Accounts Payable processes
- The benefits of automating accounts payable processes
- How to automate Accounts Payable
- Zapro – The ultimate Accounts Payable Automation PlatformÂ
What is accounts payable automation?
Accounts payable automation is when you assign innovative software and technologies to automatically perform crucial aspects that make up the accounts payable process. It includes the automation of receiving invoices, matching invoices with purchase orders, data entry, obtaining approvals, and making payments. AP automation helps adopters avoid the redundancies, inefficiencies, inaccuracies, and compliance issues that may arise if these tasks were performed manually.Â
How does AP automation work?
Simply put, why should your employees suffer with manual document handling, data entry, and paper-based workflows when the entire process can be automated by accounts payable software—Especially when software can leverage cutting-edge AI (Artificial Intelligence), ML (Machine Learning), and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to work faster and make fewer errors than a human being?Â
A thought to ponder while we walk you through the stages of the AP automation workflow.
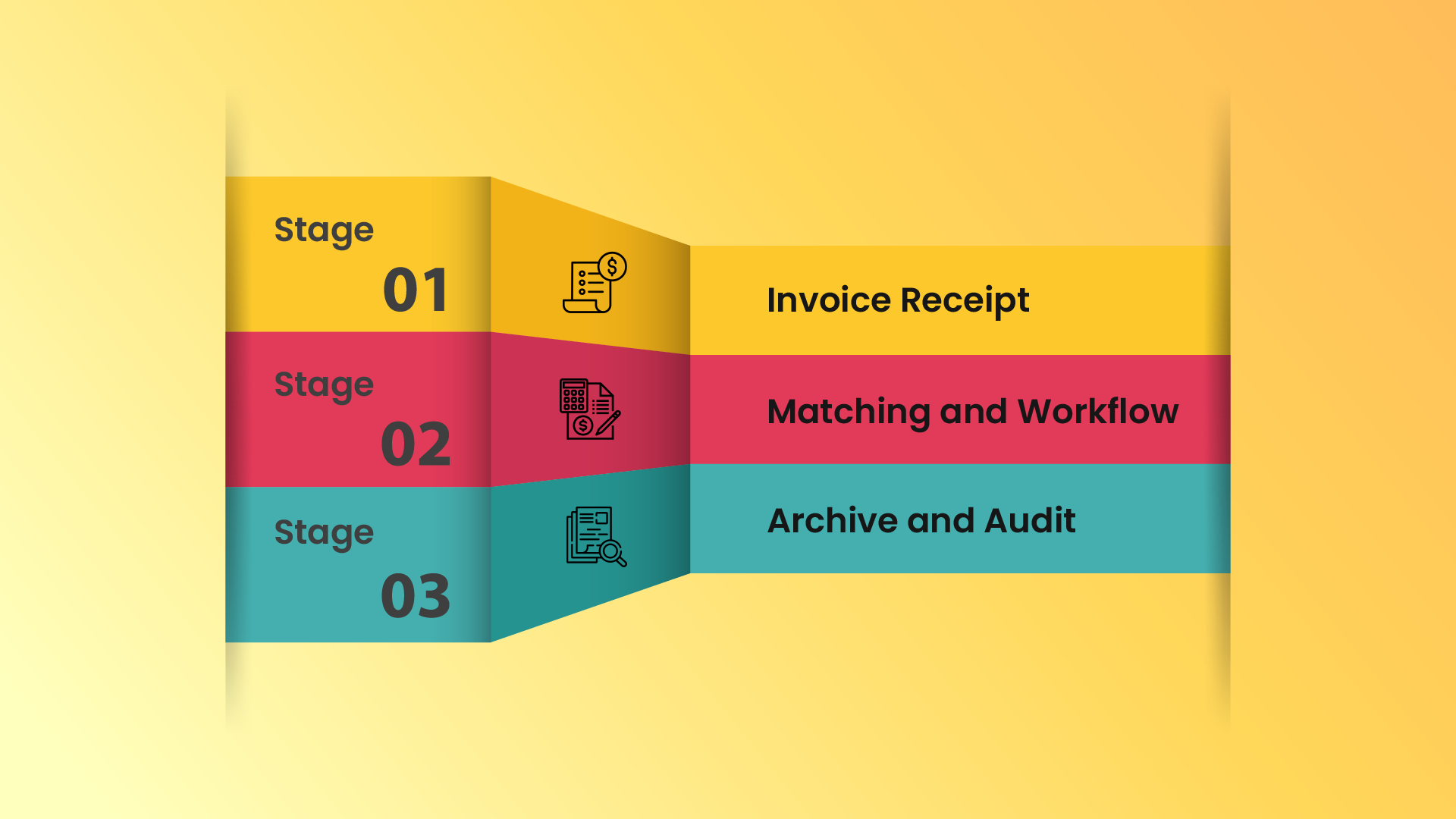
Stage 1: Invoice Receipt
The AP automation process begins when you receive the invoice. It can be paper or digital, depending on your vendors and suppliers’ format. AP automation enables you to capture the most relevant information from these invoices, convert it into data, and automatically integrate it into the automated AP system.Â
This means your employees need not manually enter expense data into tedious spreadsheets or forms. It also eliminates the need to store and manage physical copies of invoices. Once they are digitally captured, you do not need them anymore.Â
Stage 2: Matching and Workflow
Next, the automated AP system processes and matches the captured data to the corresponding POs. Here, the item, amount paid, quantity, payment terms, shipping terms, and all other relevant details of every expense are unified and recorded in one place.Â
When discrepancies arise, the system will quickly identify them and alert managers and the relevant finance department for review. Once they are resolved comes the workflow stage, where the various departmental managers and supervisors must review and grant approvals for the relevant e-invoices.
Stage 3: Archive and Audit
After the designated managers approve the invoices, the AP automation system archives them. These archives are handy for businesses having difficulties maintaining audit trails. With AP automation, the archived invoices are stored electronically and can be easily indexed, searched, and retrieved for a seamless and hassle-free external and internal audit experience.Â
Manual vs Automated Accounts Payable processes
To understand how manual and automated accounts payable processes differ, take a look at this tabular column highlighting their most prominent differences:
The benefits of automating accounts payable processes
Now that you have a better understanding of what AP automation is how it differs from manual AP processes, let us dive into some of its notable benefits.Â
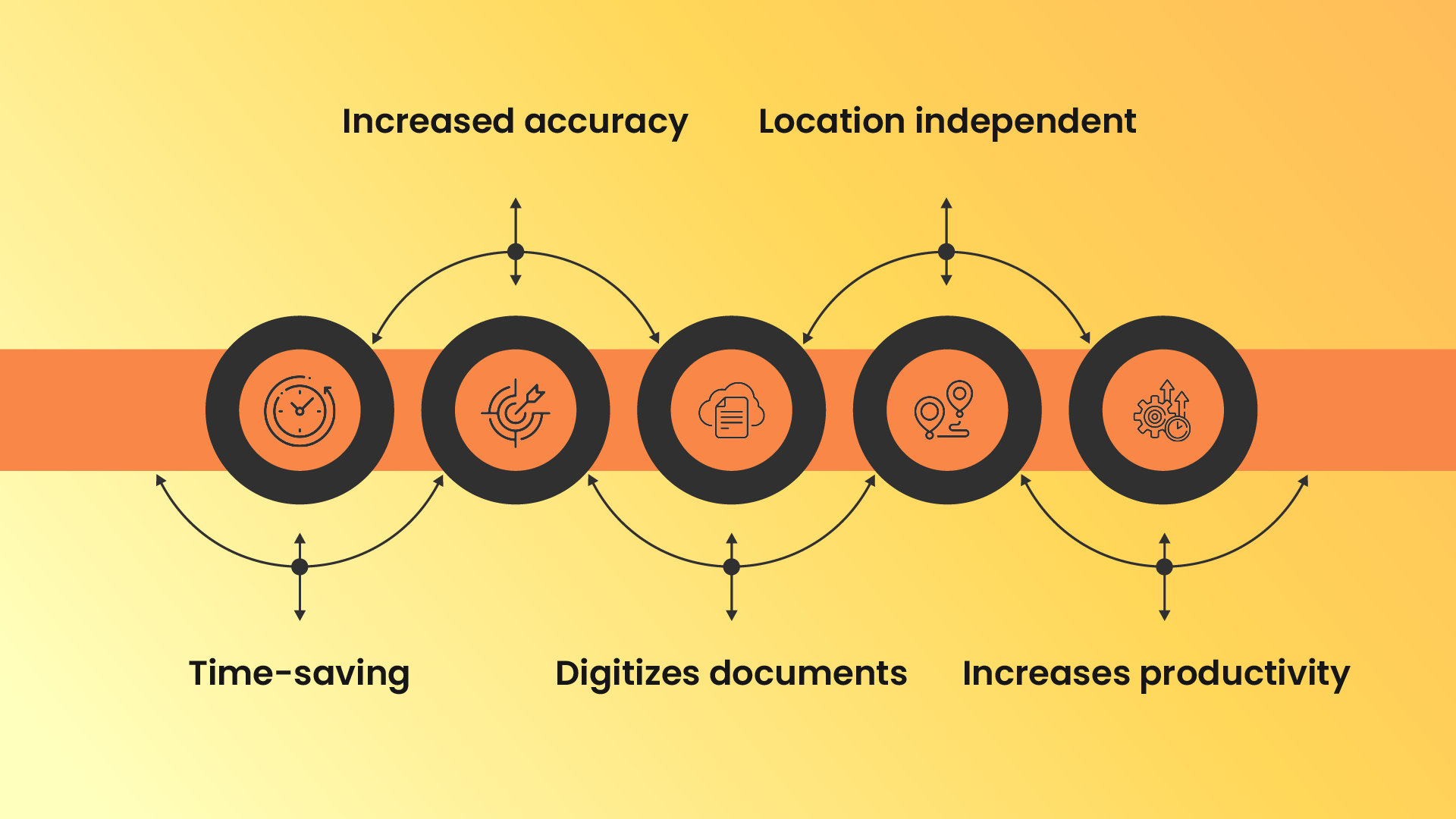
1. Time-saving
Time is the most valuable resource for any organization. When your employees and AP managers are regularly bogged down due to redundant processes or fixing problems arising from inaccuracies, accounts payable automation may be the solution for you.Â
Accounts payable automation dramatically reduces the time your employees spend on manual tasks. By freeing up your workforce, you will have additional resources that can be used to improve other competencies.Â
2. Increased accuracy
Human error is the most unfavorable byproduct of manual accounts payables processes. Manual data entry is known to cause severe bookkeeping and reporting errors that can cause the business legal and financial repercussions.Â
Instead, accounts payable automation dramatically reduces the probability of human errors by capturing and recording accurate information. When you have accounts payable automation software driven by OCR technology, you can rest assured that you accurately record the crucial information from your AP invoices and documents.
3. Digitizes documents
Going digital with accounts payable automation means you no longer need to dedicate office space solely for invoice and document storage. All your AP managers need to do is keep track of the large volume of invoices that are automatically and accurately recorded for approvals.Â
4. Location independent
Another benefit of digitization is that by storing all AP department data in a decentralized online location, your physical presence is not required to retrieve the data you need. Instead, it will always be accessible to you from anywhere in the world.Â
An intelligent automated account payable software will quickly retrieve the exact information you need when you need it. Your AP managers and employees can request all the accounts payable information they need from wherever they are.Â
5. Increases productivity
With a fully automated AP workflow, you allow yourself access to robust data that can be used for advanced analytics. You have complete control and visibility into how your automated AP processes perform in terms of KPIs such as payment trends, processing times, and cash flow forecasting. This enables you to identify redundancies, optimize working capital, and negotiate better deals with your vendors.Â
How to automate Accounts Payable
Let us dive into a step-by-step overview of how to automate accounts payable:
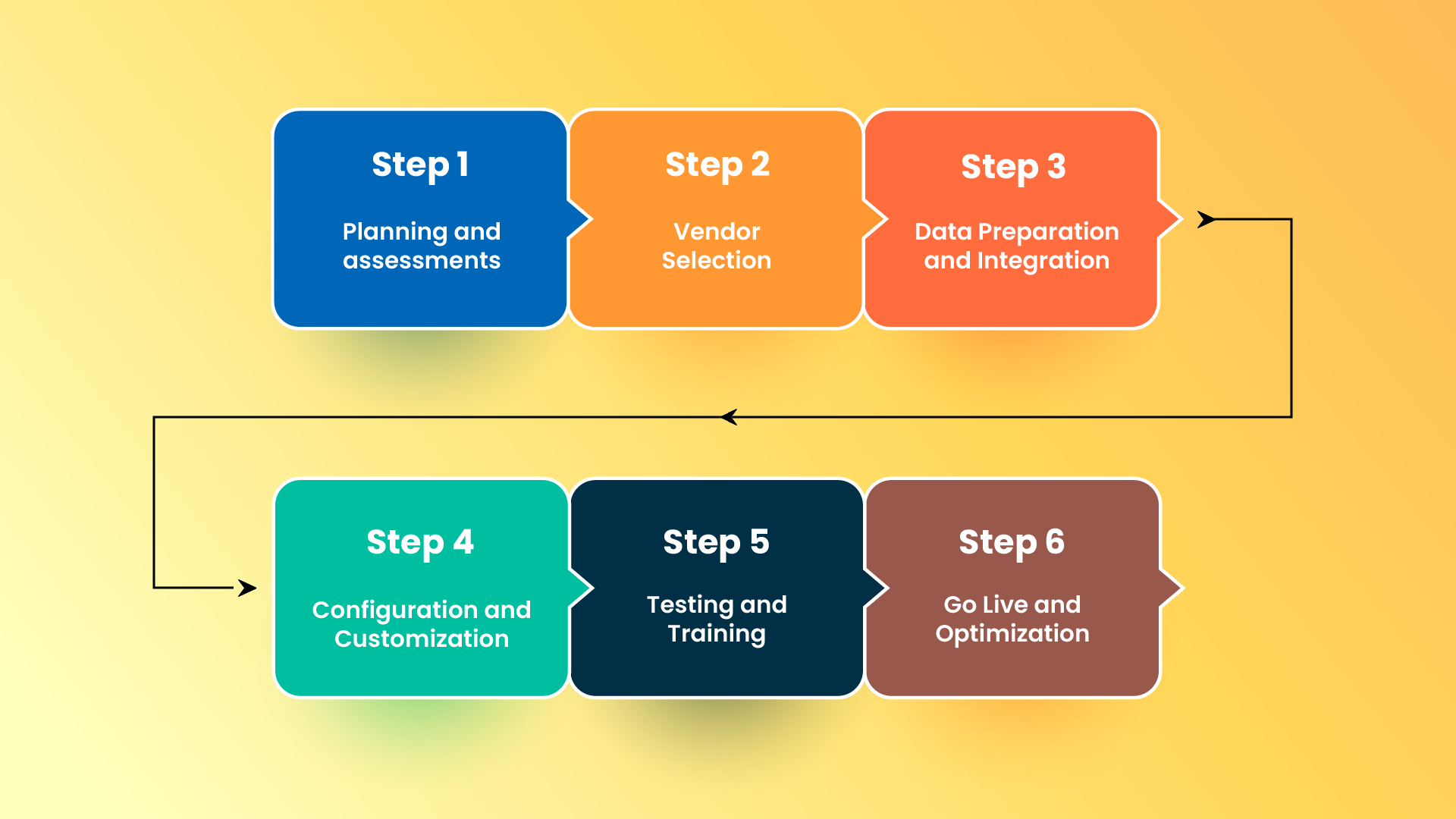
Step 1: Planning and assessments:
- Analyze and assess the strengths and shortcomings of your current systems. Take note of all the pain points that are hindering the accounts payable process.
- Determine your expectations for your AP automation. Set realistic goals and objectives that accurately reflect what you hope to achieve. For instance, if your assessment of your current systems pinpoints a lack of efficiency, query handling, and visibility, you can prioritize fixing these as the primary goals for your AP automation.Â
- Establish the proper set of KPIs to assess your AP automation project. Doing so can help you track if your project is generating the desired results regarding factors such as invoice processing time, cost per invoice, or early payment discounts.Â
- It allows you to streamline your AP automation project dynamically by altering the timelines, budget, resource allocations, and milestones to achieve your goals quicker and more efficiently
Step 2: Vendor Selection
- Before engaging in AP automation, find a service provider whose software is compatible with your existing systems. This will help you avoid the time and costs required to invest in new systems.
- When shortlisting the AP software providers, consider functionality, scalability, integration capabilities, user-friendliness, vendor reputation, and customer reviews.Â
- Prepare and issue requests for proposals (RFPs) to shortlisted vendors, outlining your requirements, budget constraints, and implementation timeline.
- Review and evaluate the received proposals, considering pricing, implementation support, customization options, and ongoing customer support.
- Select the vendor that best aligns with your requirements and negotiate contract terms.
Step 3: Data Preparation and Integration
- Before migrating to a new automated accounts payable system, you must ensure your existing AP data is clean and well organized.
- Integrate the new AP automation software with existing ERP, Financial, and document management systems to seamlessly exchange data between them.Â
Step 4: Configuration and Customization
- Configure the AP automation system to reflect your desired invoice routing and approval hierarchies.
- Define user roles and permissions within the system to ensure appropriate access levels and segregation of duties.
- Customize the system to match your business needs by configuring fields, notifications, reminders, and reports.
Step 5: Testing and Training
- For any system to be successful, it must be extensively tested with the players that will be using it the most. So ensure you engage your finance team, IT department, and other critical stakeholders in the new automated AP system so that they grow accustomed to it. Conduct extensive user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure the automation system functions as expected. Test various scenarios, including invoice entry, approval workflows, payment processing, and reporting.
- Train the AP team and other relevant stakeholders on effectively using the new system. Address any concerns, provide documentation, and communicate the benefits of the automation to gain user acceptance.
Step 6: Go Live and Optimization
- Roll out the AP automation system to production. Monitor closely during the initial period to address any issues that may arise.
- Regularly evaluate and optimize the AP process by analyzing key performance metrics, obtaining user feedback, and implementing necessary enhancements or adjustments.
- Maintain a strong relationship with the automation vendor for ongoing support, system updates, and addressing any technical issues.
Following these steps and carefully planning and implementing an integration strategy ensures a smoother rollout with fewer issues. These steps will allow you to identify flaws and perfect the system by correcting its shortcomings.Â
Over time and a few iterations, you will have a perfectly functioning system. While these actions are a good start, the most important step is to partner with the right accounts payable automation partner.Â
Zapro – The ultimate Accounts Payable Automation Platform
Zapro is the world’s first AI-powered automation tool explicitly designed to take your accounts payable process to a whole new level.Â
Our platform is consistent and standardized to process bring a whole new dimension of financial control, compliance, improved accuracy, and efficiency into your AP processes.Â
Engage in Zapro to maintain dynamic audit travels and enhance data security with minimal usage of paper-based document filling and storage.Â
Take the time to evaluate your needs, consider the features and benefits of each provider, explore our offerings in comparison, and make an informed choice that aligns with your organization’s goals and objectives.