Efficiency and accuracy are universal goals across industries, and one groundbreaking technology that has made a significant impact is Straight-Through Processing (STP).Â
While STP is widely recognized for its applications in the financial sector, its benefits extend beyond finance and into various domains.
STP represents a game-changing solution that automates and streamlines transaction processes from start to finish. In this article, we’ll explore what STP is, the benefits of STP, and the industries that typically use STPs.
What is Straight-Through Processing?
Straight-Through Processing (STP) is a technology-based approach that automates and streamlines the entire process of handling transactions without manual intervention. It involves the smooth transfer of information and instructions from the start to the end of a transaction, with little or no human involvement.
In STP, data is entered electronically at the beginning, like when a trade is executed or an order is placed. This data is then sent electronically, following set rules and standards, to the relevant systems or parties involved in the transaction. These systems can include banks, payment processors, or other intermediaries.
The main goal of STP is to eliminate the need for manual data re-entry or checking, which can lead to mistakes, delays, and extra costs. By automating the entire process, STP reduces risks, improves data accuracy, and boosts efficiency.
STP covers different stages of a transaction, like executing, confirming, matching, settling, reconciling, and reporting. It relies on seamless integration between systems, using standard data formats and communication protocols for smooth operation.
Benefits of Straight-Through Processing
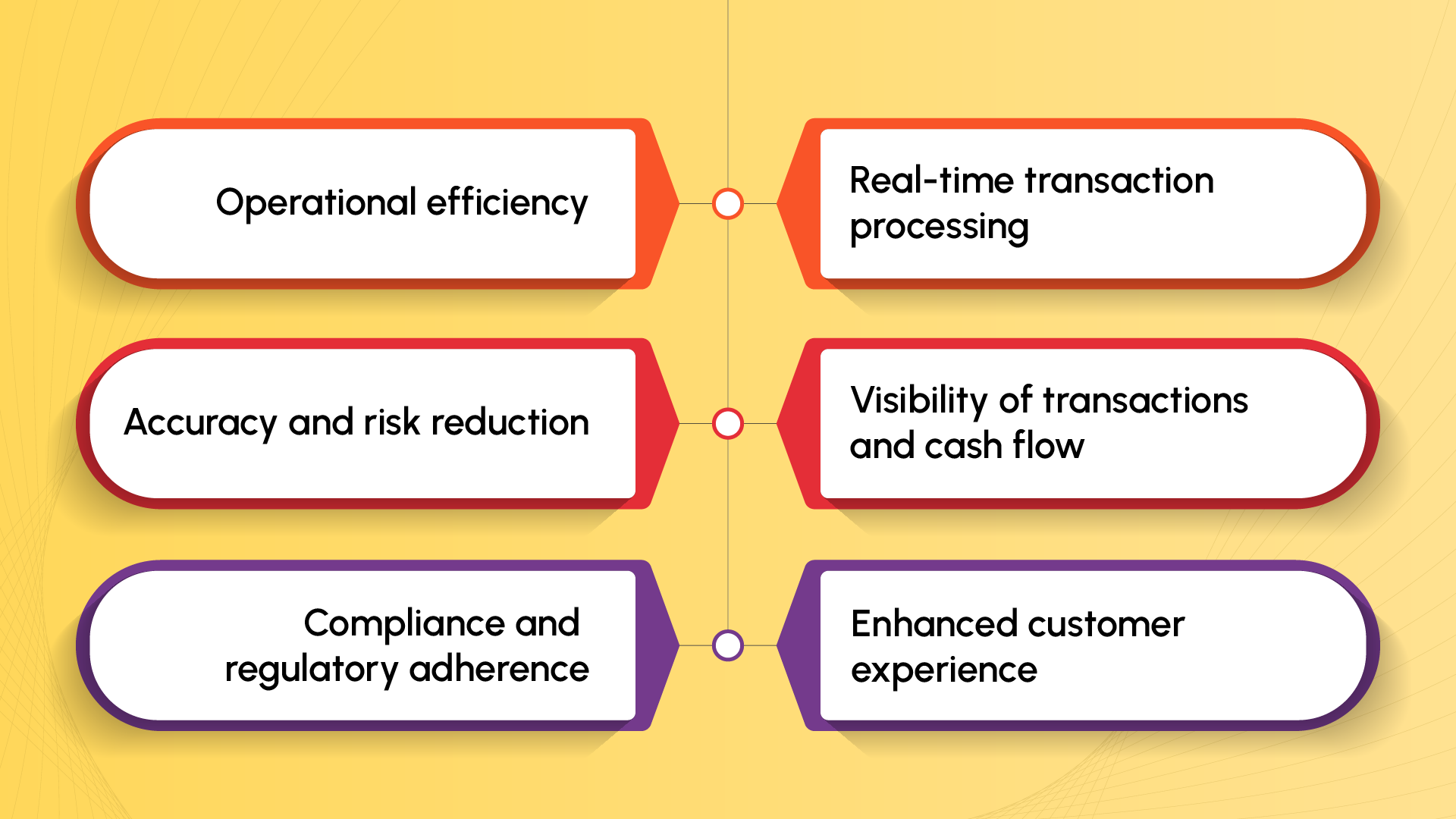
STP offers a range of comprehensive benefits that significantly enhance transaction processing across industries. The benefits include the following.
- Operational efficiency
- Real-time transaction processing
- Accuracy and risk reduction
- Visibility of transactions and cash flow
- Compliance and regulatory adherence
- Enhanced customer experience
1. Operational efficiency
STP eliminates manual intervention, reducing the time-consuming tasks of rekeying data and manual checks. By automating processes, STP streamlines workflows, minimizes errors, and accelerates transaction handling.Â
This increased efficiency leads to significant cost savings, improved productivity, and enhanced competitiveness.Â
STP replaces cumbersome manual processes with streamlined automation, enabling organizations to process transactions faster, reduce operational bottlenecks, and achieve higher operational efficiency.
2. Real-time transaction processing
STP enables transactions to be processed promptly, ensuring near-instantaneous execution and settlement.Â
Whether it’s executing trades, settling payments, or managing complex transactions, STP ensures transactions are processed in a timely manner, reducing risks associated with time lags and enhancing overall operational agility.
Unlike traditional processes that can take days to complete, STP empowers organizations with real-time transaction processing capabilities. Real-time processing minimizes delays, providing organizations with a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment.
This eliminates the waiting periods associated with manual intervention and ensures faster transaction execution, reducing the risk of missed opportunities and enhancing overall operational agility.
3. Accuracy and risk reduction
With STP, the risk of human errors is significantly reduced. By eliminating manual data re-entry and verification, STP minimizes the potential for data entry mistakes, omissions, or misinterpretations.Â
Automated validation checks and standardized processes further enhance data accuracy, ensuring that transactions are processed correctly. This reduces the risk of errors that can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and compliance issues.Â
STP’s accuracy and risk reduction measures help reduce operational and settlement risks, safeguard against financial losses, and protect the reputation of the organization.
4. Visibility of transactions and cash flow
STP provides organizations with comprehensive visibility into the status of transactions and cash flow. Real-time tracking and reporting capabilities allow for accurate monitoring of transactions at every stage, from initiation to settlement.Â
This visibility enables organizations to have a clear understanding of their cash flow position, facilitating effective decision-making, forecasting, and financial planning.Â
With real-time updates and visibility, organizations can proactively manage cash flow, optimize working capital, and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
5. Compliance and regulatory adherence
STP helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and adhere to compliance standards. By automating processes and enforcing predefined rules, STP ensures consistent adherence to regulations.Â
This reduces the risk of non-compliance, potential penalties, and reputational damage.Â
STP enables organizations to maintain audit trails, ensure accurate record-keeping, and generate the necessary reports to demonstrate compliance with regulatory frameworks.Â
This is particularly crucial in industries where compliance with regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements, is essential.
6. Enhanced customer experience
STP plays a vital role in enhancing the customer experience by enabling faster transaction processing. Real-time updates, shorter processing times, and reduced errors contribute to a smoother and more efficient customer journey.Â
Customers benefit from the timely execution of their transactions, reduced waiting periods, and improved service delivery. STP empowers customers with real-time transaction tracking, ensuring transparency and trust.Â
Enhanced customer experience leads to higher customer loyalty, positive word-of-mouth, and increased business opportunities for organizations.
7. Benefits international payments processing
In the context of international processing, STP facilitates the seamless exchange of information and funds across borders, overcoming geographical barriers and complexities associated with international transactions.Â
The standardized data formats and communication protocols used in STP ensure consistent and accurate data exchange, promoting efficiency, reducing costs, and supporting international trade activities.Â
By enabling faster and more reliable cross-border transactions, STP enhances global business operations, fosters international collaboration, and opens doors to new markets.
Which industries typically use STP?
STP finds its application in various industries where efficient and streamlined transaction processing is crucial. The industries that typically require STP are those with high transaction volumes, complex workflows, and a need for real-time data exchange.Â
By automating end-to-end processes and minimizing manual intervention, STP improves operational efficiency, reduces errors, and enhances overall productivity.Â
Let’s explore some of the key industries that extensively utilize STP and understand how it benefits them.
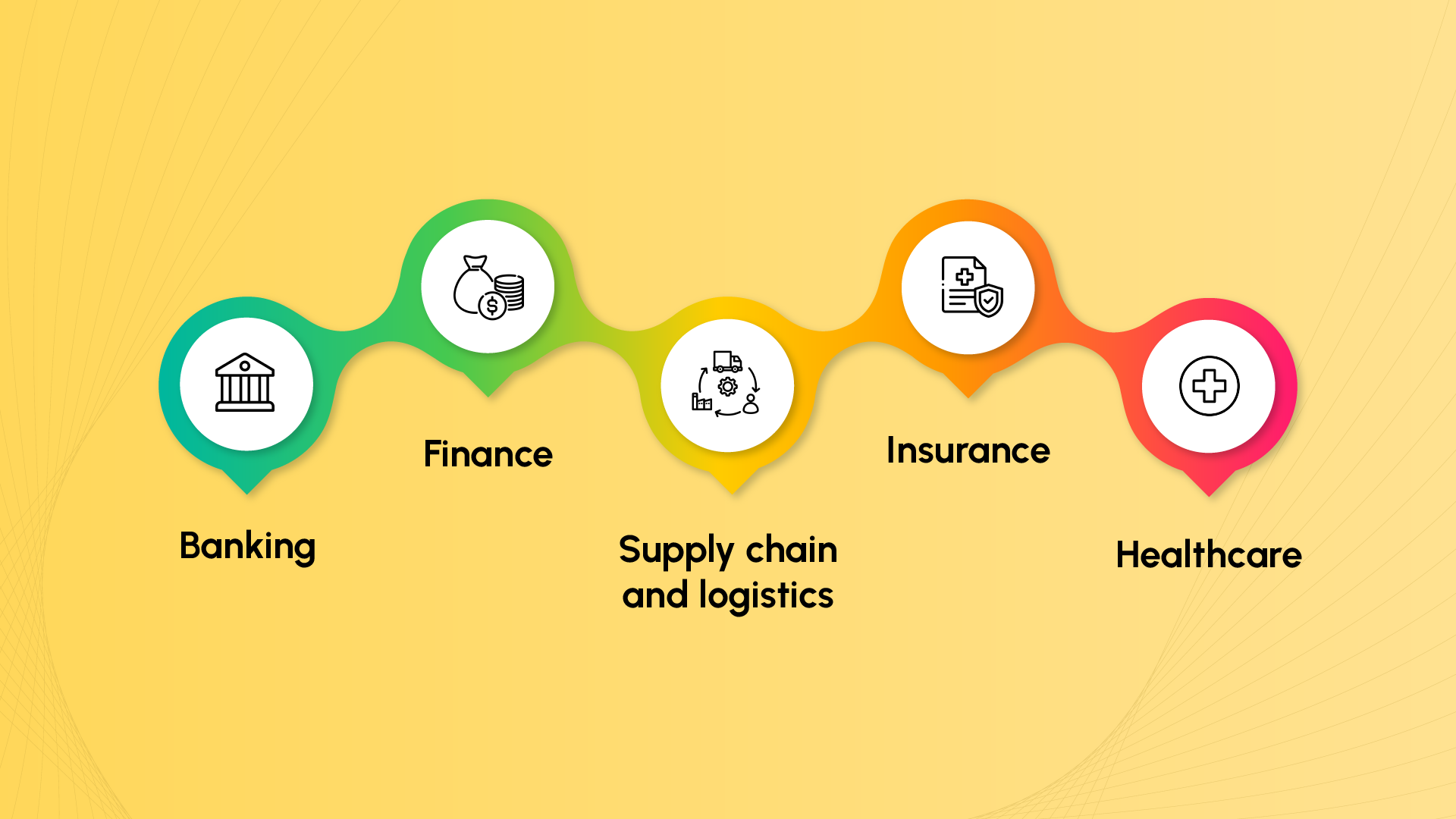
1. Banking
The banking industry extensively utilizes STP due to its complex and high-volume transaction processing requirements.Â
STP enables banks to automate various processes such as payment processing, fund transfers, account management, and trade execution. It helps banks improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, minimize errors, and enhance customer service by providing real-time transaction updates.Â
Additionally, STP ensures compliance with regulatory standards and facilitates seamless integration with other financial systems.
2. Finance
The finance industry, including investment firms, asset managers, and trading companies, heavily rely on Straight-Through Processing (STP) to streamline trading, portfolio management, and settlement processes.Â
STP enables real-time trade capture, confirmation, and settlement, reducing errors and shortening settlement timeframes. By automating complex financial workflows, STP enhances operational efficiency and improves overall trading performance.Â
It replaces manual processes, allowing orders to be processed, confirmed, cleared, and settled almost instantly, eliminating the need for physical stock certificates. STP has revolutionized the finance industry, but wider adoption is needed for it to become universal.
3. Supply chain and logistics
In supply chain and logistics, STP plays a crucial role in automating and optimizing the movement of goods and information.Â
It enables the seamless integration of various stakeholders, such as manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and transportation providers, by automating processes like order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking.Â
STP improves supply chain visibility, enhances coordination, reduces errors, and accelerates order fulfillment, resulting in improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
4. Insurance
STP is widely used in the insurance industry to automate policy administration, claims processing, underwriting, and premium collection.Â
By eliminating manual intervention, STP accelerates the entire insurance lifecycle, enabling insurers to process policies and claims more efficiently.Â
It enhances accuracy, reduces administrative costs, provides real-time visibility into policy status, and enables faster claims settlement, leading to improved customer experience and operational effectiveness.
5. Healthcare
The healthcare industry employs STP to streamline administrative processes, such as medical billing, claims processing, and electronic health record (EHR) management.Â
STP automates the flow of information between healthcare providers, insurers, and patients, improving accuracy, reducing billing errors, and expediting claim settlement.Â
It enhances data security, simplifies compliance with healthcare regulations, and supports efficient healthcare service delivery.
While STP offers significant benefits to these industries, it may not be suitable for all sectors. STP is not typically recommended for companies with lower transaction loads or tight budgets.Â
Implementing STP involves significant upfront costs for technology infrastructure, software systems, and training. For companies with limited transaction volume or financial resources, the return on investment may not justify these expenses.Â
Additionally, the complexity and potential benefits of STP may not outweigh the costs for companies with lower transaction volumes. Allocating resources and ongoing maintenance can be challenging for companies with tighter budgets.Â
It is important for companies to assess their transaction volume, budget, and operational requirements, considering alternative solutions that align with their needs and resource constraints.Â
To wrap up,
In a world where efficiency and accuracy are paramount, Straight-Through Processing (STP) has emerged as a transformative force across industries.Â
By automating and streamlining transaction processes from start to finish, STP offers a multitude of benefits that enhance operational efficiency, reduce risks, and elevate customer experience.Â
From the financial sector to supply chain logistics, insurance, and healthcare, STP has proven its versatility and effectiveness. While not suitable for all companies, those with high transaction volumes and a focus on optimization can harness the power of STP to propel their businesses forward.Â
As technology continues to advance, embracing STP’s potential will undoubtedly pave the way for a more efficient and productive future.